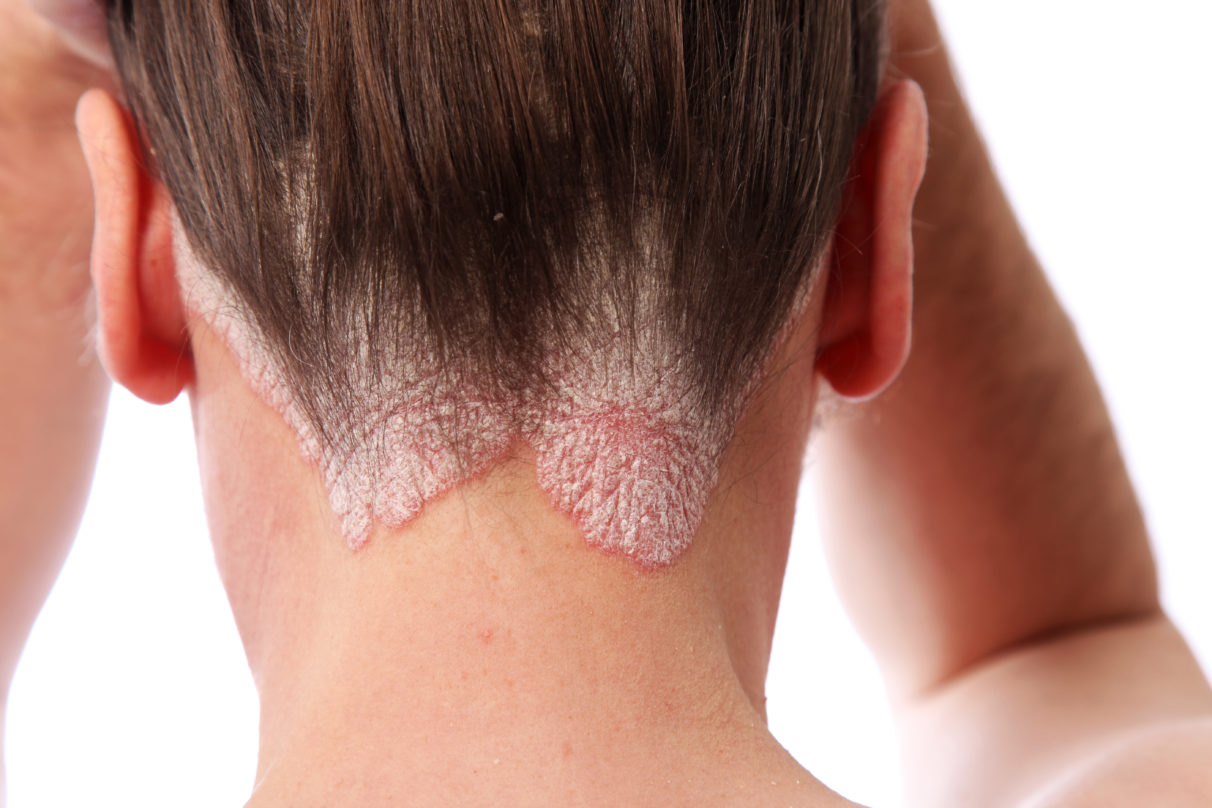
Access to treatment
Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis is treated in basic health care in cases where the disease is well controlled. Co-morbidity treatment is also included in basic health care.
Dermatology specialists treat patients who have uncertain diagnosis, rash that does not calm down with appropriate local therapy, or skin psoriasis that is expanding rapidly. Specialists also treat patients with difficult psoriasis or psoriasis that causes disability.
Systemic treatment of skin psoriasis is initiated and monitored by a specialist in dermatology. The safety and efficacy of treatment should be closely monitored. Biological treatment is initiated and monitored by a specialist in dermatology or rheumatic diseases.
Specialists in rheumatology treat patients with new inflammation that affects more than four joints (polyarthritis), illness resembling ankylosing spondylitis, or prolonged inflammation in up to four joints, to which anti-inflammatory agents and local cortisone injections have little impact, or which show progressive changes in x-ray. Children and pregnant women suffering from psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis are treated at specialized medical care.
Treatment guarantee
Psoriasis treatment is covered by the treatment guarantee. This means that patients must have immediate access to treatment at a health care centre during office hours on weekdays. The law for securing access to treatment determines the period of time in which a municipal resident must have access to in medically necessary, non-emergency diagnostic or therapeutic care. The need for treatment is assessed by a health care professional. They should assess the need for treatment within three working days of the patient’s initial contact. In specialized medical care, evaluation of the need for treatment must begin within three weeks of referral. In basic health care, the patient must be granted treatment within three months from the evaluation. The need for treatment is estimated on the basis of a referral. If the tests show that you need hospitalization, it must begin no later than six months after the assessment of the need for treatment.
